International
WHO launches call to speed up genomics tech development
International
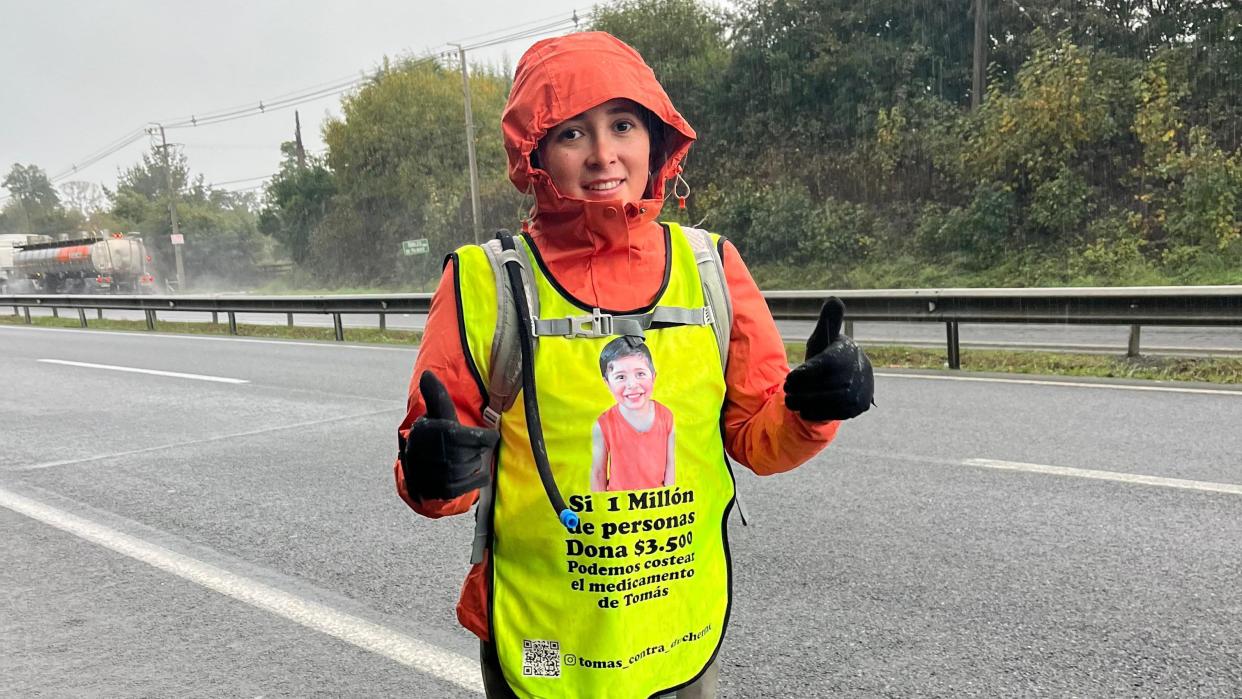
The mother who decided to walk 1,300 kilometers in Chile to get an expensive medicine and save her son from a serious illness
International
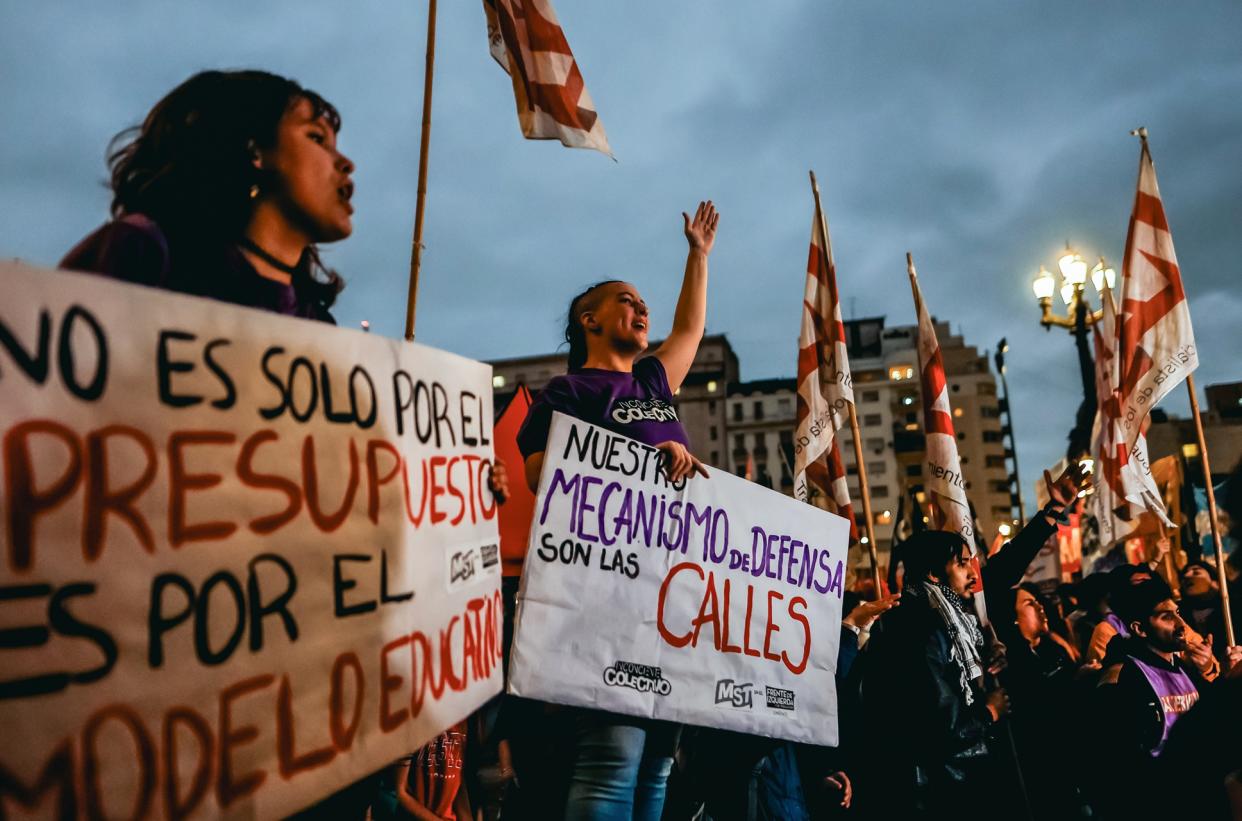
Commissions of the Argentine Senate resume debate on key law for Javier Milei
International
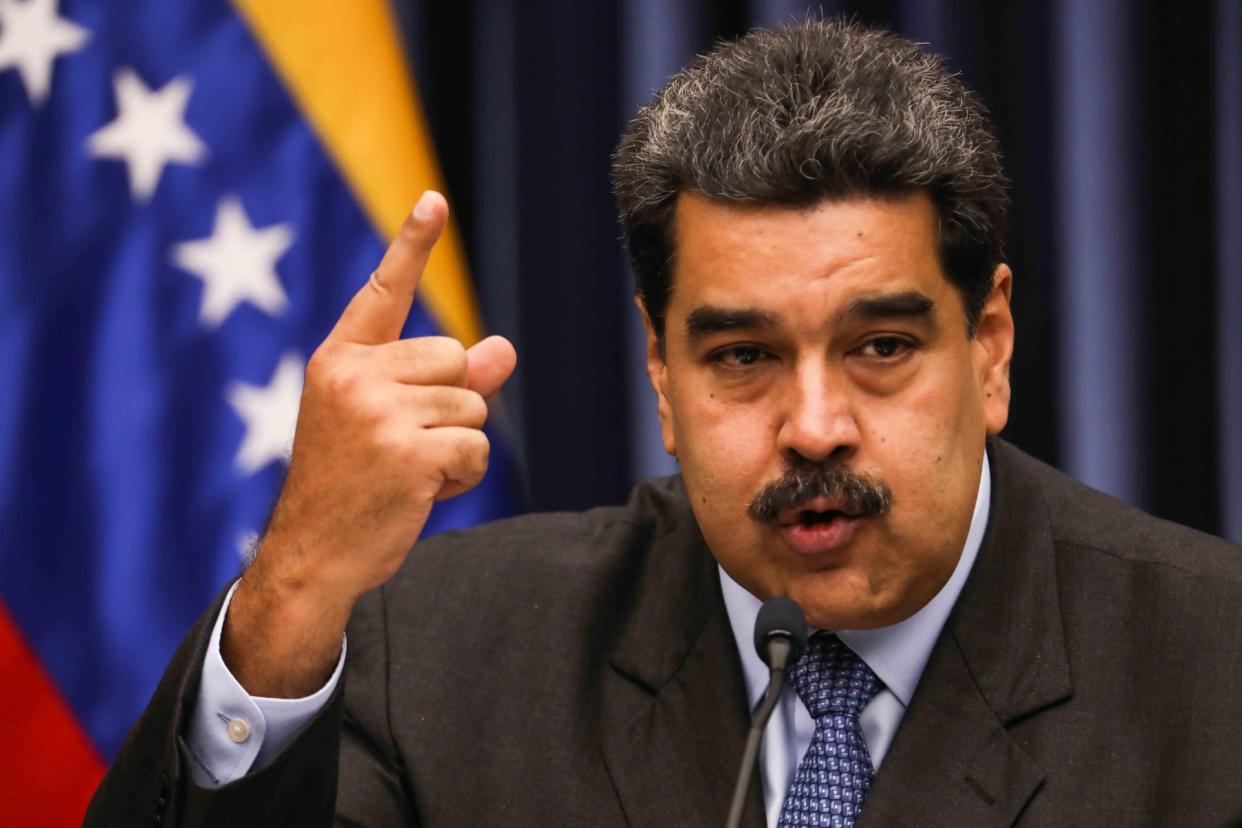
Former presidents condemn Maduro’s “disrespect” of asylum for opponents in Venezuela
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoPetro calls former President Duque a “terrorist” for the “murder” of young people in protests
-
 International2 days ago
International2 days agoFirst recipient of genetically modified pig kidney dies two months post-transplant
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days ago14 of the injured left by a train crash in Buenos Aires are still interned
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoMIT students protest again despite reprisals from the center and Biden’s accusation
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoAn aurora borealis is visible tonight from much of Spain
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoFormer Peruvian President Alberto Fujimori, diagnosed with a new malignant tumor
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days ago‘No to animal abuse’, the clamor of a march of dogs and humans in Bolivia
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoDonald Trump faces former lawyer in court over Stormy Daniels payments
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoDuque sees “despair” and “insecurity” in Petro’s attitude and proposes a “democratic debate”
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoHaitian armed gangs mobilize before the arrival of the multinational force
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoThe Emir of Kuwait dissolves Parliament and suspends some clauses of the Constitution
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoDeath toll from storms in southern Brazil rise to 137
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoFormer presidents condemn Maduro’s “disrespect” of asylum for opponents in Venezuela
-

 Sin categoría5 days ago
Sin categoría5 days agoThey reject the request of former Honduran president Juan Orlando Hernández for a new trial in New York
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoColombian Foreign Minister on the accusation of Diosdado Cabello: To foolish words, deaf ears
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoThe UN confirms that a worker died in Gaza from a projectile that hit his vehicle
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoTrump criticizes pro-Biden Jews: “If you vote for him, be ashamed”
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoCommissions of the Argentine Senate resume debate on key law for Javier Milei
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoBrian Wilson, of The Beach Boys, is under the tutelage of his manager because of his dementia
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoThe mother who decided to walk 1,300 kilometers in Chile to get an expensive medicine and save her son from a serious illness
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoThe UN says it works with the de facto Afghan Government to assist in floods
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoTrump, portrayed by his former lawyer: Fixation for silencing porn actress and reluctant to pay
-

 International20 hours ago
International20 hours agoA Mexican-American artist denounces the deportations with a mural on the border
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoThe FARC dissident ‘Iván Márquez’ reappears in a video after being presumed dead
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoThe president-elect of Panama, José Raúl Mulino, promises repatriation of migrants crossing the Darién
























