International
North Korea launches an intermediate-range missile, its first test in two months
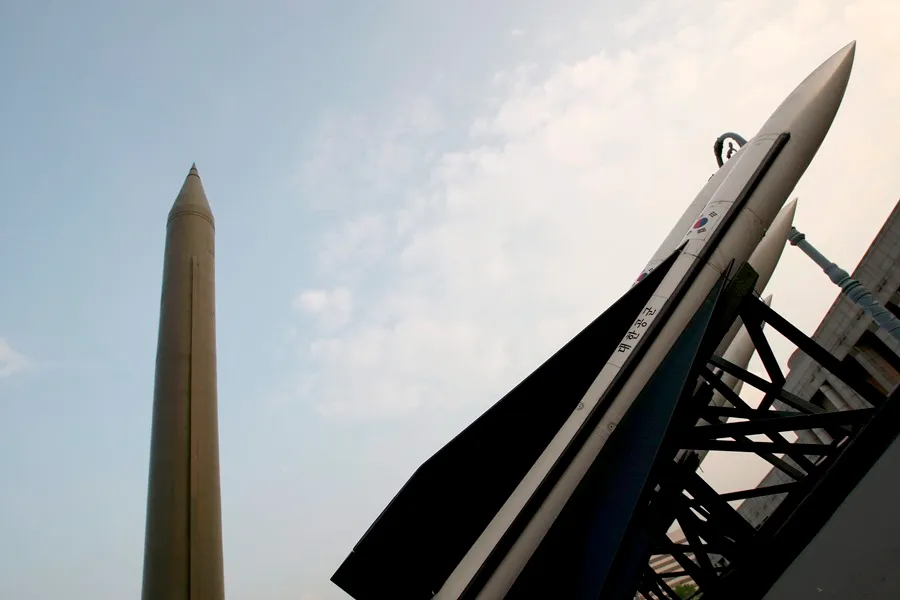

North Korea launched this Monday what is believed to be an intermediate range ballistic missile (IRBM) into the Sea of Japan (called the East Sea in the two Koreas), in what is its first test of this type in two months.
“Our army detected a ballistic missile launched from the Pyongyang area around 12:00 today (3:00 GMT),” the South Korean Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) reported in a statement.
“The missile fell into the East Sea after flying approximately 1,100 kilometers,” the text adds.
The regime’s last weapons test occurred on November 5 when Pyongyang launched several short-range missiles.
This Monday’s launch occurred after 12:00 (3:00 GMT) and was also confirmed by the Japanese Ministry of Defense, which detected the new North Korean weapons test and pointed out that the projectile has already fallen out of its exclusive economic area (EEZ).
The Japanese government has formed a special team to collect information and study possible damage, according to government spokesman Yoshimasa Hayashi.
The first missile launched in 2025
Today’s is the first missile launched by North Korea in 2025 and the last launch after those that occurred on November 5, and which were attributed to an attempt to provoke by the regime in view of the presidential elections in the United States.
Then, the North launched several short-range ballistic missiles with a maximum height of 100 km and that covered a distance of about 400 km.
The essay also coincides with the visit of the US Secretary of State, Antony Blinken, to Seoul, in what will be his last trip to the Asian country in office, before the arrival of Donald Trump to the US Presidency.
On October 31, Pyongyang also launched an ICBM that traveled a distance of about 1,000 kilometers from its launch point in the interior of North Korea to fall into waters north of Japan, reaching a maximum height of 7,000 kilometers, according to data collected by Tokyo and Seoul.
The Japanese Ministry of Defense pointed out that this projectile was the one that had flown the longest before its impact (one hour and 25 minutes), while a military source from Seoul said it was the largest missile tested to date by Pyongyang.
North Korea said it was a new Hwasong-19 model projectile and described it as an “irreversible” achievement in its nuclear weapons development.
International
Florida judge sets 2027 trial in Trump’s $10 billion lawsuit against BBC

A federal judge in Florida has scheduled February 2027 for the trial in the lawsuit filed by U.S. President Donald Trump against the BBC, in which he is seeking $10 billion in damages for defamation.
Trump accuses the British broadcaster of airing a misleading edit of a speech he delivered on January 6, 2021, which, he says, made it appear that he explicitly urged his supporters to attack the U.S. Capitol in Washington.
The president filed the suit in December in federal court in Florida, alleging defamation and violations of a law governing business practices when the program was broadcast ahead of the 2024 election.
Trump is seeking $5 billion in damages for each of the two claims.
Lawyers for the BBC unsuccessfully asked the court to dismiss the case, arguing that Trump had not suffered a “legally recognizable harm,” since the investigative program Panorama, which included the edited footage, aired outside the United States.
International
Head-of-state diplomacy key to guiding China–U.S. ties, Beijing says

Head-of-state diplomacy plays an irreplaceable strategic guiding role in China–United States relations, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Lin Jian said on Thursday during a regular press briefing, when asked about high-level exchanges between the two sides.
Lin added that in a recent phone call, U.S. President Donald Trump once again expressed his intention to visit China in April, while Chinese President Xi Jinping reiterated his invitation.
Both sides remain in communication regarding the matter, the spokesperson said.
Lin noted that the essence of China–U.S. economic and trade ties lies in mutual benefit and win-win outcomes.
“Both parties should work together to implement the important consensus reached by the two heads of state, injecting greater certainty and stability into China–U.S. economic and trade cooperation, as well as into the global economy,” he said.
International
Trump administration to end special immigration operation in Minnesota

The administration of Donald Trump is bringing to a close its special operation targeting illegal immigration in the northern state of Minnesota, border czar Tom Homan announced Thursday, following weeks of unrest and the fatal shootings of two activists by federal agents.
Thousands of federal officers had been deployed to Minnesota in December to carry out large-scale raids against undocumented immigrants.
The operations triggered strong reactions from residents and advocacy groups, leading to daily confrontations and the deaths of two people who were shot by federal agents.
“I proposed, and President Trump agreed, that this special operation should end in Minnesota,” Homan said during a press conference in the state capital, Minneapolis.
“A significant drawdown began this week and will continue into next week,” he added.
Homan indicated that similar enforcement efforts could be launched in other cities.
“Next week we will redeploy the agents currently here back to their home stations or to other parts of the country where they are needed. But we will continue to enforce immigration laws,” he said.
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoGuatemala isolates Barrio 18 leader after attacks that killed 11 police
-
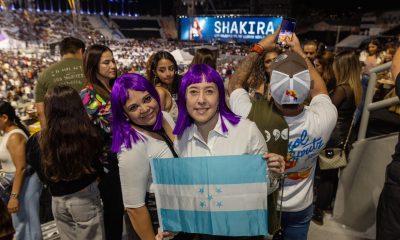
 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoShakira ignites El Salvador with near sold-out residency at Mágico González Stadium
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoU.S. Health Department says CDC grants no longer match agency priorities
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoOver 50 Civil Groups Urge House to Impeach DHS Secretary Kristi Noem
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoICE Arrests Reach 379,000 Under Trump, Testimony Shows Amid Minnesota Shootings
-

 Central America1 day ago
Central America1 day agoGuatemala to Phase Out Longstanding Medical Cooperation Agreement with Cuba
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoDespite homicide drop, overall deadly violence remains high in Mexico: study
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoSheinbaum Urges Mexico to ‘Jealously’ Guard Sovereignty at Air Force Anniversary
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoJet Fuel Crisis Hits Cuba: Flights Disrupted, Air Canada Cancels Services
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMEPs Approve Plan That Could Fast-Track Rejection of Some Asylum Claims
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoNew York’s New Archbishop Names Óscar Romero as His Favorite Saint
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMexico Rises Slightly to 141st in Global Corruption Perceptions Index 2025
-

 International3 hours ago
International3 hours agoFlorida judge sets 2027 trial in Trump’s $10 billion lawsuit against BBC
-

 International3 hours ago
International3 hours agoTrump administration to end special immigration operation in Minnesota
-

 International3 hours ago
International3 hours agoHead-of-state diplomacy key to guiding China–U.S. ties, Beijing says
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoExclusive Tucson Neighborhood Shaken by Disappearance of Savannah Guthrie’s Mother
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoChile Unveils Latam-GPT to Give Latin America Its Own AI Model


























