International
Tackling hunger in Haiti, the arduous task of the World Food Program
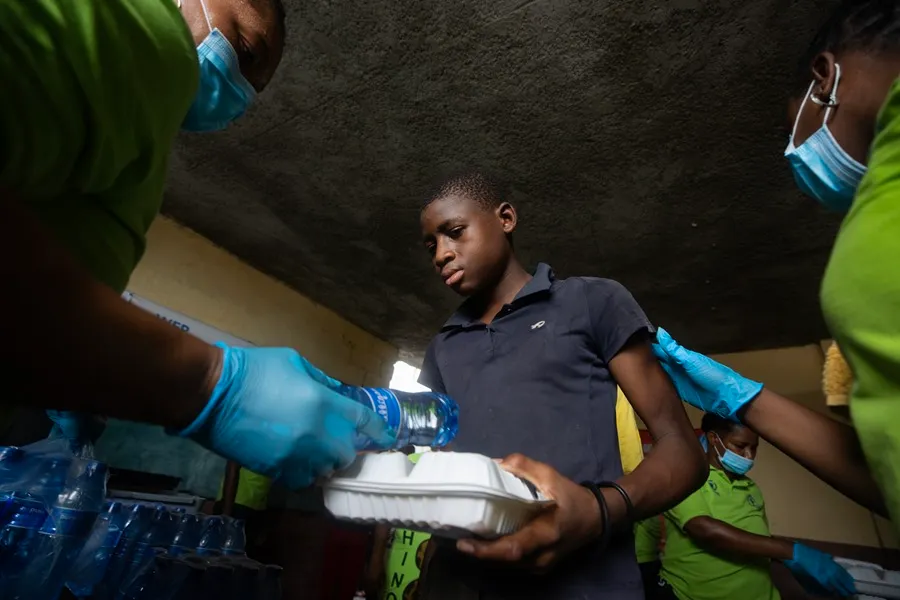
In the Central Kitchen of the World Food Program (WFP) in the capital of Haiti, dozens of people work against the clock to fight hunger: some cut food, others cook in huge pots, some carry trays in vehicles to deliver them to the camps where thousands of families wait for that plate of food, sometimes the only one of the day.
One of those shelters is the Isidor Jean Louis School, in the center of Port-au-Prince, which has been welcoming 600 refugees for months after leaving their homes due to the violence of the armed gangs. There EFE accompanies the WFP.
One of those staying at that hostel is Elva Senfró, 85 years old. He has been there for months after fleeing the neighborhood by his son in the middle of a cruel gang attack.
“The gang was attacking the neighborhood, burning the houses, and my son ran me out of the place and brought me to school, where I have been living for five months (…) I would like to eat something every day, but it is not like that, it is only possible when they bring me something,” this old woman tells EFE.
In Haiti, about five million people (almost half of the population) face acute food insecurity and, of them, 1.64 million face “emergency” levels, according to the data handled by WFP. They are the highest rates since the 2010 earthquake, which caused about 300,000 deaths.
In recent years, Haiti has experienced a steady increase in hunger, and the prevalence of acute food insecurity went from 35% in 2019 to almost 50% in 2024.
Something that the director of the WFP in Haiti, Jean-Martin Bauer, insists on in statements to EFE: “There are five million people who have difficulty getting food. They are people who don’t know what they are going to eat tomorrow, who don’t have money to know if they are going to eat the next day.”
Among the most affected areas is the Artibonite Valley, considered the country’s barn and where armed groups have seized agricultural land and stolen crops.
The department of the West, the rural areas of the south and several poor neighborhoods of the capital, such as Croix des Bouquets and Cité Soleil, with important hotbeds of hunger, are also a cause for concern.
“Artibonite is an area that produced a lot of food for the country and now they themselves have nothing to eat, due to the violence,” explains Bauer, who estimates that there are 3,000 producers who cannot cultivate the land and abandoned it due to the violence of the gangs.
Around two in the afternoon, the staff of the Center for Peasant Animation and Community Action (CAPAC), one of the local organizations with which the WFP works, arrive at the Isidor Jean Louis College.
It is an operation that they carry out daily: some quickly go to school and take the food to a room on the second floor, while others organize the refugees to proceed with the delivery of lunch.
The little ones lead the line, and they are followed by the elderly and pregnant women. They receive a tray of rice with fish and a bottle of water.
The rest of middle-aged people, between pushing and arguments, take a long time to organize to enter the room. When the food is already in his hands, everyone goes to the place of the school where he resides and eats in silence, enjoying every bite.
“The population wants security. People who go to church with the children, who go to school, who go to the market, are afraid and are leaving little because they don’t want to be kidnapped on the street. The population doesn’t deserve that, it deserves a better life,” says Bauer.
And he adds: “Those of us who work on the humanitarian issue would like to see freedom of movement on the street. If there is so much hunger, it’s because the producers can’t get to sell to the capital. We want to see the producers leave the Artibonite and enter the capital to sell their products. That they bring good food to the markets. That is the most important issue for the food system.”
International
U.S. Senate Rejects Budget, Bringing Government Closer to Shutdown Amid DHS Dispute

The U.S. Senate voted on Thursday against a budget proposal in a move aimed at pressuring changes at the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), following the killing of two civilians during a deployment of immigration agents in Minneapolis.
All Senate Democrats and seven Republican lawmakers voted against the bill, which requires 60 votes to advance, pushing the country closer to a partial government shutdown that would cut funding for several agencies, including the Pentagon and the Department of Health.
The rejection came as Senate leaders and the White House continue negotiations on a separate funding package for DHS that would allow reforms to the agency. Proposed measures include banning Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents from wearing face coverings and requiring them to use body-worn cameras during operations.
The vote took place just hours after President Donald Trump said he was “close” to reaching an agreement with Democrats and did not believe the federal government would face another shutdown, following last year’s record stoppage.
“I don’t think the Democrats want a shutdown either, so we’ll work in a bipartisan way to avoid it. Hopefully, there will be no government shutdown. We’re working on that right now,” Trump said during a Cabinet meeting at the White House.
International
Trump Says Putin Agreed to One-Week Halt in Attacks on Ukraine Amid Extreme Cold

U.S. President Donald Trump said on Thursday that he secured a commitment from Russian President Vladimir Putinto halt attacks against Ukraine for one week, citing extreme weather conditions affecting the region.
“Because of the extreme cold (…) I personally asked Putin not to attack Kyiv or other cities and towns for a week. And he agreed. He was very pleasant,” Trump said during a Cabinet meeting broadcast by the White House.
Trump acknowledged that several advisers had questioned the decision to make the call.
“A lot of people told me not to waste the call because they wouldn’t agree. And he accepted. And we’re very happy they did, because they don’t need missiles hitting their towns and cities,” the president said.
According to Trump, Ukrainian authorities reacted with surprise to the announcement but welcomed the possibility of a temporary ceasefire.
“It’s extraordinarily cold, record cold (…) They say they’ve never experienced cold like this,” he added.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky later commented on the announcement, expressing hope that the agreement would be honored.
International
Storm Kristin Kills Five in Portugal, Leaves Nearly 500,000 Without Power
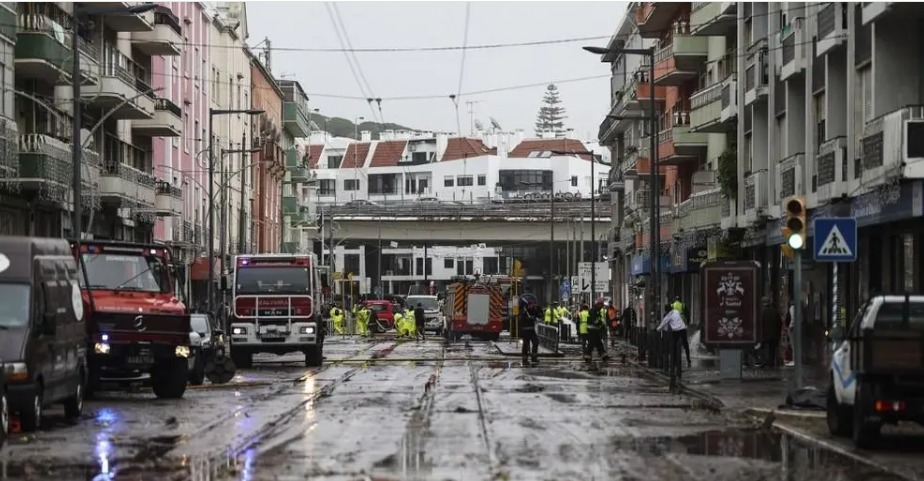

Storm Kristin, which battered Portugal with heavy rain and strong winds early Wednesday, has left at least five people dead, while nearly half a million residents remained without electricity as of Thursday, according to updated figures from authorities.
The revised death toll was confirmed to AFP by a spokesperson for the National Emergency and Civil Protection Authority (ANPEC). On Wednesday, the agency had reported four fatalities.
Meanwhile, E-Redes, the country’s electricity distribution network operator, said that around 450,000 customers were still without power, particularly in central Portugal.
Emergency services responded to approximately 1,500 incidents between midnight and 8:00 a.m. local time on Wednesday, as the storm caused widespread disruptions.
The Portuguese government described Kristin as an “extreme weather event” that inflicted significant damage across several regions of the country. At the height of the storm, as many as 850,000 households and institutions lost electricity during the early hours of Wednesday.
Several municipalities ordered the closure of schools, many of which remained shut on Thursday due to ongoing adverse conditions.
Ricardo Costa, regional deputy commander of the Leiria Fire Brigade, said residents continue to seek assistance as rainfall persists.
“Even though the rain is not extremely intense, it is causing extensive damage to homes,” he noted.
In Figueira da Foz, a coastal city in central Portugal, strong winds toppled a giant Ferris wheel, underscoring the severity of the storm.
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoGuatemala Police Arrest Prison Guard Caught in the Act of Extortion
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoHonduras swears in conservative president Asfura after disputed election
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoBukele leads public trust rankings as UCA survey highlights gains in security
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoFootball Fan Killed in Clashes After Colombian League Match
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoDoomsday clock moves to 85 seconds before midnight amid rising global risks
-

 Central America3 days ago
Central America3 days agoGuatemala President Says Starlink Terminal Found Inside Prison
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoWinter Storm Fern Leaves 30 Dead and Over One Million Without Power Across the U.S.
-

 Sin categoría4 days ago
Sin categoría4 days agoEight Killed in Series of Armed Attacks in Ecuador’s Manabí Province
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoU.S. Senate Rejects Budget, Bringing Government Closer to Shutdown Amid DHS Dispute
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoSpain approves plan to regularize up to 500,000 migrants in Historic Shift
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoMissing Spanish Sailor Rescued After 11 Days Adrift in Mediterranean
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoRubio Says U.S. Could Participate in Follow-Up Russia-Ukraine Talks
-

 Sin categoría4 days ago
Sin categoría4 days agoEl Salvador Launches Fourth Year of Ocean Mission to Protect Marine Ecosystems
-

 Central America22 hours ago
Central America22 hours agoPanama Supreme Court Strikes Down Panama Ports Concession as Unconstitutional
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoStorm Kristin Kills Five in Portugal, Leaves Nearly 500,000 Without Power
-

 Central America22 hours ago
Central America22 hours agoU.S. and Guatemala Sign Trade Deal Granting Zero Tariffs to Most Exports
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMan Arrested After Vehicle Crashes Into Jewish Institution in Brooklyn
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump Says Putin Agreed to One-Week Halt in Attacks on Ukraine Amid Extreme Cold








































