International
Chilean scientist plans to clean up mining with ‘metal eating’ bacteria
AFP
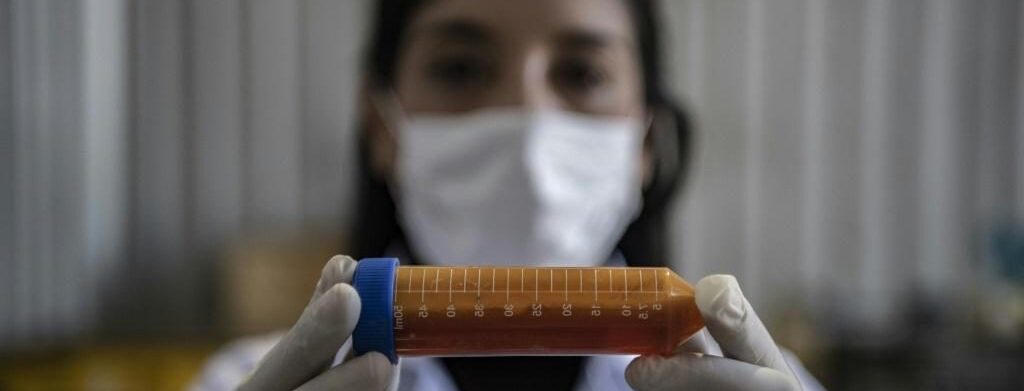
Starving microorganisms capable of surviving in extreme conditions have already managed to “eat” a nail in just three days.
In Chile, a scientist is testing “metal-eating” bacteria she hopes could help clean up the country’s highly-polluting mining industry.
In her laboratory in Antofagasta, an industrial town 1,100-kilometers north of Santiago, 33-year-old biotechnologist Nadac Reales has been carrying out tests with extremophiles — organisms that live in extreme environments.
Reales came up with her idea while still at university as she was conducting tests at a mining plant using microorganisms to improve the extraction of copper.
“I realized there were various needs in the mining industry, for example what happened with the metallic waste,” she told AFP.
Some metals can be recycled in smelting plants but others, such as HGV truck hoppers that can hold 50 tons of rock, cannot and are often discarded in Chile’s Atacama desert, home to the majority of the country’s mining industry.
Chile is the world’s largest producer of copper, which accounts for up to 15 percent of the country’s GDP, resulting in a lot of mining waste that pollutes the environment.
In her research, Reales, who now runs her own company Rudanac Biotec, concentrated on iron-oxidizing bacteria called Leptospirillum.
She extracted the bacteria from the Tatio geysers located 4,200 meters above sea level, some 350 kilometers from Antofagasta.
The bacteria “live in an acidic environment that is practically unaffected by relatively high concentrations of most metals,” she said.
“At first the bacteria took two months to disintegrate a nail.”
But when starved, they had to adapt and find a way of feeding themselves.
After two years of trials, the result was a marked increase in the speed at which the bacteria “ate,” devouring a nail in just three days.
– Surprising benefit –
Reales says “chemical and microbiological tests” have proved the bacteria are not harmful to humans or the environment.
“We’ve always seen a lot of potential in this project that has already passed an important test in the laboratory,” said Drina Vejar, a microbiologist who is part of a four-person team working with Reales.
“It’s really necessary at this time when we have to plan for a more sustainable development, especially in all these cities with so many polluting industries.”
Mining companies have shown interest in the research but while Rudanac Biotec previously benefitted from a state fund for start-ups, the company needs investment to move on to its next stage of trials.
Reales says she needs money to see if her method will “eat a medium sized beam or a hopper.”
When the disintegration process is complete, what remains is a reddish liquid residue, a solution known as a lixiviant that itself possesses a surprising quality.
“After biodisintegration the product generated (the liquid) can improve the recovery of copper in a process called hydrometallurgy,” said Reales.
Essentially, the liquid residue can be used to extract copper from rock in a more sustainable manner than the current use of chemicals in leaching.
Reales says it means green mining is “totally feasible.”
That is of great interest to mining companies that could use it to improve their large scale extraction of copper or other minerals, while also reducing their pollution, something they are required to do by law.
Reales recently submitted a request for an international patent for her technology, but more importantly she hopes it will help reduce metal waste blotting the landscape in the mining regions of her country.
International
Mexico, Brazil and Colombia left out of Trump’s “Shield of the Americas” summit
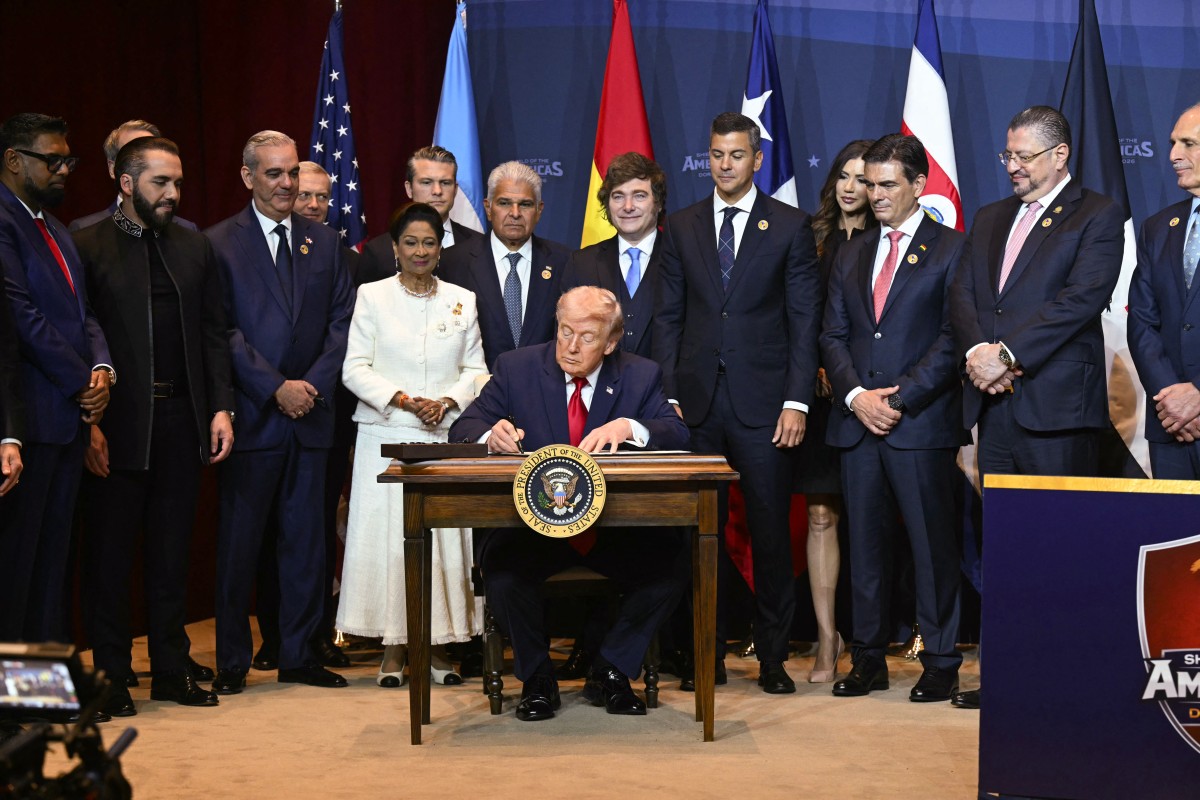

Left-wing governments in Latin America, including Mexico, Brazil and Colombia, were excluded from the “Shield of the Americas” summit convened by U.S. President Donald Trump.
The meeting, held in Miami, Florida, brought together 12 presidents from across the continent to discuss strategies to combat drug cartels and organized crime.
In Mexico’s case, President Claudia Sheinbaum had recently rejected the use of military force as a solution to the drug trafficking problem. She has argued that her administration’s security strategy is producing results and emphasized that force alone is not the answer.
During the summit, Trump said that most narcotics entering the United States come through Mexico and referred to his previous conversations with Sheinbaum on the issue.
“I like the president very much, she’s a very good person,” Trump said. “But I told her: ‘Let me eradicate the cartels.’ And she said, ‘No, no, no, please, president.’ We have to eradicate them. We have to finish them.”
The remarks highlighted ongoing differences between Washington and Mexico over how to confront drug trafficking networks operating across the region.
International
Trump announces 17-nation alliance in the Americas to “destroy” drug cartels

U.S. President Donald Trump announced on Saturday the creation of a 17-nation alliance across the Americas aimed at dismantling drug cartels, during a regional summit held at his golf club in Doral.
Speaking to a group of allied leaders at the Shield of the Americas Summit, Trump said the initiative would rely on military force to eliminate powerful criminal networks operating throughout the hemisphere.
“The heart of our agreement is the commitment to use lethal military force to destroy these sinister cartels and terrorist networks. Once and for all, we will put an end to them,” Trump told the assembled heads of state.
The Republican leader argued that large portions of territory in the Western Hemisphere have fallen under the control of transnational gangs and pledged U.S. support to governments seeking to confront them. He even suggested the potential use of highly precise missiles against cartel leaders.
Before making the announcement, Trump greeted the roughly twelve leaders attending the summit, including close allies such as Javier Milei, Daniel Noboa and Nayib Bukele, whom he described as a “great president.”
The meeting forms part of Trump’s broader regional strategy inspired by his reinterpretation of the Monroe Doctrine, which seeks to reinforce Washington’s influence in the Americas, strengthen security cooperation and counter the growing presence of powers such as China.
Trump pointed to recent U.S. actions in the region as examples of his administration’s approach, including the operation that led to the capture of former Venezuelan president Nicolás Maduro earlier this year.
The summit also takes place amid escalating international tensions following the conflict launched last week by the United States and Israel against Iran.
International
Trump replaces Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem with Senator Markwayne Mullin

U.S. President Donald Trump announced Thursday the departure of Kristi Noem as Secretary of Homeland Security, one of the key architects of the administration’s policy of deporting undocumented immigrants.
Noem, who has been assigned a new role as a “special envoy” to Latin America, will be replaced starting March 31 by Republican Senator Markwayne Mullin, the president said in a message posted on his social media platform Truth Social.
According to media reports, Trump made the decision after Noem’s recent hearings in Congress, during which she faced tough questions regarding the awarding of a major public contract.
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoClaudia Sheinbaum: Operation Against ‘El Mencho’ Was Based on Pending Arrest Warrants
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWhite House Says Spain Agrees to Cooperate with U.S. Military After Trump Threatens Trade Embargo
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoSpain Denies Any Agreement to Cooperate with U.S. Military in Iran Operations
-

 Central America5 days ago
Central America5 days agoNicaragua Held Responsible for Harassment of Opposition Prosecutor and His Family
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump announces 17-nation alliance in the Americas to “destroy” drug cartels
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoYoung Woman Will Represent Mexico at 2026 World Cup Opener, Says President Sheinbaum
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours agoMexico, Brazil and Colombia left out of Trump’s “Shield of the Americas” summit
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoTrump replaces Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem with Senator Markwayne Mullin




























